- Published 12 Jun 2023
- Last Modified 29 Aug 2023
- 6 min
What are Electrical Transformers?
Whether isolating a current or decreasing or increasing a voltage, there is a transformer for every need.

Reviewed by Mithun Subbaroybhat, Technical Support Engineer (December 2022)
Transformers are seen nearly wherever there is an electrical circuit, from power grids to office computers. But what is the function of a transformer, how do they work, and are there different types?
What Do Electrical Transformers Do?

Electrical transformers are devices sometimes referred to as passive electrical devices, that come in all shapes and sizes and are responsible for moving electrical currents between circuits. They can send current from one circuit to another or multiple circuits, depending on what the current is required for. Electrical transformers can also lower or increase the voltage being transferred to a circuit, meaning they can be used in transferring current in a range of applications and are an energy-efficient way to transfer current between circuits.
Transformers are used in both industrial settings to supply power to residential areas. Modern electrical transformers are designed to carry Alternating current and can carry high voltages across a long distance, making them ideal for transferring current powering energy grids.
How Do Electrical Transformers Work?
Electrical transformers work on the principle of Faradays Law, or to summarise they use electromagnetic induction to connect two circuits to transfer the electrical current from one circuit to the other. As previously mentioned, sometimes during the transference a voltage will be increased or reduced based on the energy need. However, the frequency over the current will always stay the same.
Electrical Transformers contain a magnetic core, a primary winding, and a secondary winding. In a transformer diagram, the structure of the transformer would look like a square (this being the core), with two wires wrapped around each vertical side (these being the primary and secondary windings). These windings have separated and isolated electrical currents, that are linked via the magnetic core in the centre. In a transformer, an electrical current will be received through the primary wire which will cause the core to create an electromagnetic field which will in turn create a voltage in the secondary wire. This voltage or current is the secondary wire is current that is sent out and completes the electrical transfer from the primary circuit to the secondary circuit.
What Does a Step-Up Transformer Do?
A step-up transformer is an electrical transformer that receives a low voltage and during transfer to another circuit, increases the voltage. Whilst the voltage increases from the primary circuit to the secondary circuit, the current value will decrease - during the process of transference, the frequency will stay the same.
A step-up electrical transformer still contains a primary winding, a secondary winding, and a magnetic core. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
This is then transferred as a voltage and current through the secondary wire, via the electromagnetic field. However, in a step-up transformer, the primary wire has a higher voltage and fewer turns around the core compared to a secondary winding. The secondary winding has a lot more turns, increasing the voltage in the secondary wire and transferring a to a new circuit that is higher in voltage and lower in current value.
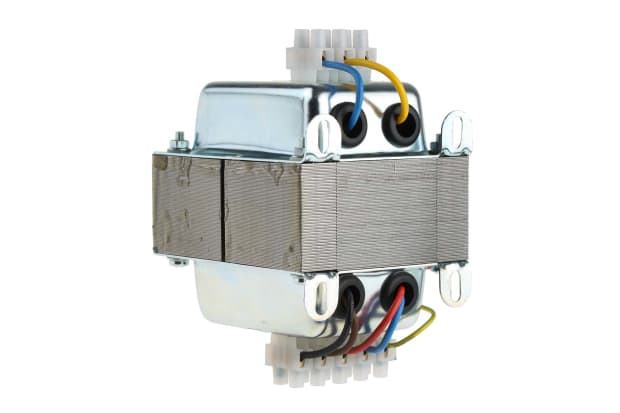
What Does a Step-Down Transformer Do?
Step-up transformers work the opposite way to step-down transformers, they instead receive a high voltage from one circuit and convert it to a low voltage, when transferring to a different circuit or circuits. The step-down transformer differs in that it will increase the current value as it decreases the voltage. However, much like a step-up transformer, the frequency will stay the same in a step-down transformer.
Plus, the step-down transformer is similar in that it contains the same internal structure. It has a primary winding, secondary winding, and metal core. It receives current in the primary winding and sends out a transferred current through the secondary winding, via the electromagnetic field created by the core. However, unlike a step-up transformer, the primary windings have more turns than the secondary windings. This reverse in structure compared to a step-up transformer helps the step-down transformer in its task of lowering the voltage as it transfers current from one circuit to another. Step-down transformers are also known as autotransformers.
Electrical Transformer Types
As well as coming in different sizes, transformers can come in different types, to suit energy needs.
Voltage Transformer
Voltage transformers can also be referred to as ‘potential transformers’. They are responsible for stepping down large voltage amounts and working in parallel with incoming currents to produce a lower voltage in outgoing currents.
Power Transformer
These are step-up transformers that raise voltage, without changing the frequency. As previously mentioned, these transformers have no moving parts and use the principle of Faradays Law to transfer current. They can be classed into three sizes which are small, medium, and large. The largest Power Transformers also need assistance with cooling to function - this being with the use of a cooling agent.
Air Coil Transformer
The third type of transformer is the air coil transformer. These transformers are used in small devices and therefore do not have a metal core to create a magnetic field of current transference. Instead, the primary and secondary windings are wrapped around a lower conductive material such as plastic or cardboard. A magnetic link between windings and air passing over the windings is then used to aid in current transference.
PCB Transformer
As per their name, these transformers are designed to work with circuit boards in computers. They isolate current and are responsible for lowering the voltage in a circuit board to a safe level.
Where are Electrical Transformers Used?
Electrical transformers are used for a wide range of tasks and in both residential and industrial settings. Electrical transformers are used in low-tech equipment such as doorbells, but can also be utilized in electronic devices, such as computers and tablets. On a larger scale, transformers can be used to help transfer current to power grids.
In terms of application, transformers can be used to stabilise and isolate currents, help measure a voltage in a circuit, balance the current in two circuits and make a circuit safe by lowering the voltage.
Whatever the application, the safety of a transformer will always need to be considered. Every transformer has a maximum voltage requirement, so this will partially determine what type of transformer is used for your desired application.